2024 Federal Budget Highlights
On April 16, 2024, Canada’s Deputy Prime Minister and Finance Minister, Chrystia Freeland, presented the federal budget.
While there are no changes to federal personal or corporate tax rates, the budget introduces:
-
An increase in the portion of capital gains subject to tax, rising from 50% to 66.67%, starting June 25, 2024. However, individual gains up to $250,000 annually will retain the 50% rate.
-
The lifetime exemption limit for capital gains has been raised to $1.25 million. Additionally, a new one-third inclusion rate is set for up to $2 million in capital gains for entrepreneurs.
-
The budget confirms the alternative minimum tax changes planned for January 1, 2024 but lessens their impact on charitable contributions.
-
This year’s budget emphasizes making housing more affordable. It provides incentives for building rental properties specifically designed for long-term tenants.
-
Introduces new support measures to aid people buying their first homes.
-
Costs for specific patents and tech equipment and software can now be written off immediately.
-
Canada carbon rebate for small business.
Capital Gains Inclusion Rate
The budget suggests raising the inclusion rate on capital gains after June 24, 2024:
-
Corporations and trusts, from 50% to 66.67%.
-
Individuals, on capital gains over $250,000 annually, also from 50% to 66.67%.
For individuals, the $250,000 annual threshold that applies to net capital gains—the amount remaining after offsetting any capital losses. This includes gains acquired directly by an individual or indirectly through entities such as partnerships or trusts. Essentially, this threshold acts as a deductible, considering various factors to determine the net gains eligible for the increased capital gains tax rate.
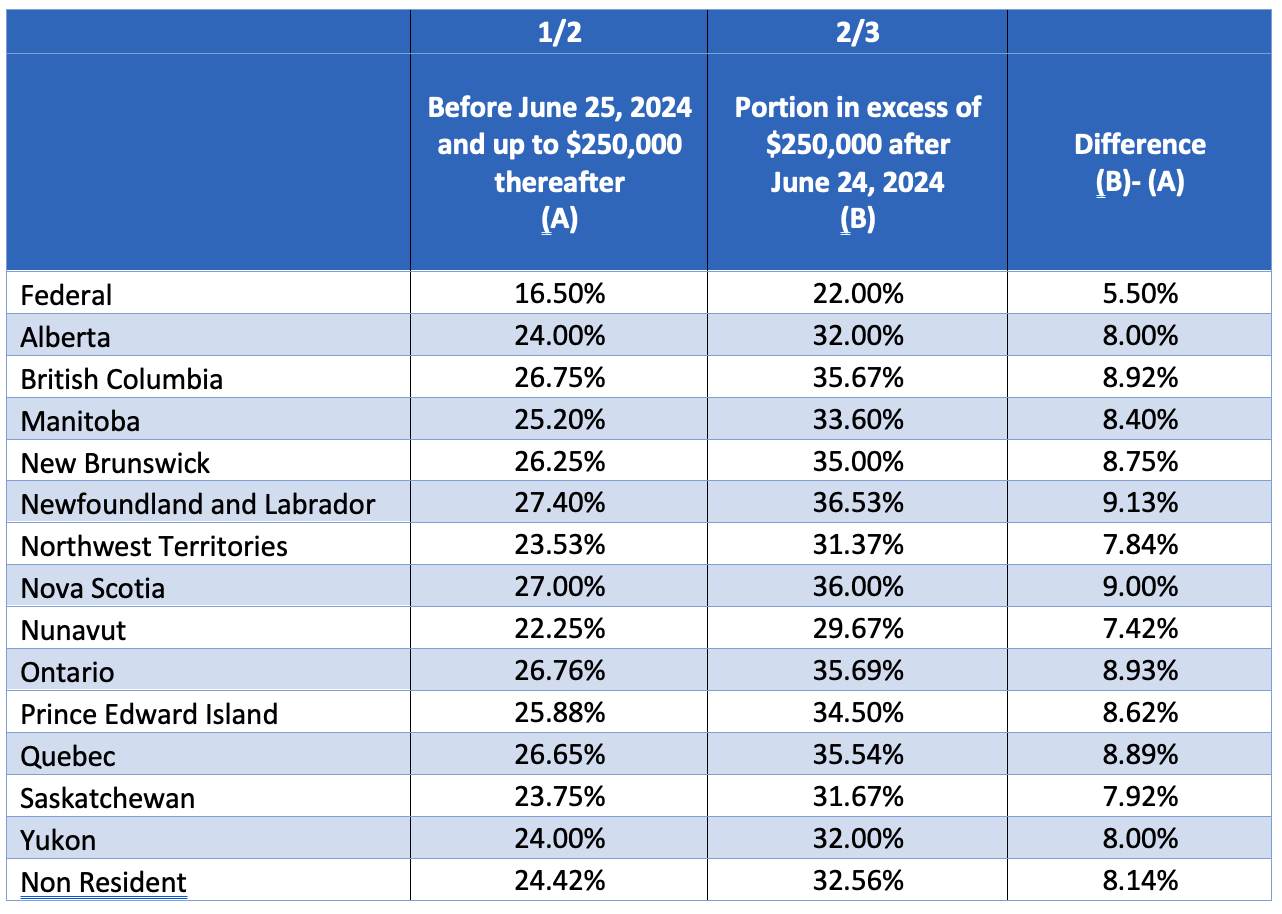
Individuals in the highest income bracket, who earn above the top marginal tax rate threshold, will face a higher tax rate on capital gains exceeding $250,000 due to these changes. Furthermore, the budget modifies the tax deduction for employee stock options to align with the updated capital gains taxation rates yet maintains the initial 50% deduction for the first $250,000 in gains. Regarding previously incurred financial losses, the budget plans to adjust the value of these net capital losses from past years so that they are consistent with the current gains, upholding the uniformity with the new inclusion rate.
The budget outlines transitional rules for the upcoming tax year that straddles the implementation date of the new capital gains rates. If the tax year begins before June 25, 2024, but ends afterward, capital gains realized before June 25 will be taxed at the existing rate of 50%. However, gains accrued after June 24, 2024, will be subject to the increased rate of 66.67%. It’s important to note that the new $250,000 threshold for higher tax rates will only apply to gains made after June 24.
Consequently, for individuals earning capital gains beyond the $250,000 threshold and who fall into the highest income tax bracket, new rates will be effective as outlined in the table below. Specifically, this pertains to individuals with taxable incomes exceeding $355,845 in Alberta, $252,752 in British Columbia, $1,103,478 in Newfoundland and Labrador, $500,000 in the Yukon, and $246,752 in all other regions.
Further details and guidance on these new rules are expected to be provided in future announcements.
Lifetime Capital Gains Exemption
The budget proposes raising the Lifetime Capital Gains Exemption (LCGE) for qualified capital gains from $1,016,836 to $1.25 million, effective for sales made after June 24, 2024. Additionally, the exemption will once again be adjusted for inflation starting in 2026. This change aims to increase the tax benefits for individuals selling certain types of property, such as small business shares or farming and fishing assets.
Canadian Entrepreneurs’ Incentive
The Canadian Entrepreneurs’ Incentive is a new tax measure which provides a reduced inclusion rate on capital gains from the disposition of qualifying small business shares.
Qualifications for the incentive include:
-
Shares must be of a small business corporation directly owned by an individual.
-
For 24 months before selling, over half the corporation’s assets must be actively used in a Canadian business or be certain connected assets.
-
The seller needs to be a founding investor who held the shares for at least five years.
-
The seller must have been actively involved in the business continuously for five years.
-
The seller must have owned a significant voting share throughout the subscription period.
-
The incentive does not apply to shares linked to professional services, financial, real estate, hospitality, arts, entertainment, or personal care services sectors.
-
The shares must have been acquired at their fair market value.
-
The incentive allows for a reduced inclusion rate of 1/3 for up to $2 million in capital gains during an individual’s lifetime, with this limit being phased in over 10 years.
This measure will apply to dispositions after December 31, 2024.
Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT)
The 2023 budget included updates to the AMT, with proposed changes outlined in the summer of 2023. The budget suggests revising the charitable donation tax credit for AMT calculations, increasing the claimable amount from 50% to 80%.
Further proposed changes to the AMT include:
-
Permitting deductions for the Guaranteed Income Supplement, social assistance, and workers’ compensation benefits.
-
Exempting employee ownership trusts (EOTs) entirely from AMT.
-
Allowing certain tax credits, like federal political contributions, investment tax credits (ITCs), and labour-sponsored funds tax credit, to be carried forward if disallowed under the AMT.
These changes would take effect for tax years beginning after December 31, 2023. Additionally, the budget proposes technical amendments that would exempt specific trusts benefiting Indigenous groups from the AMT.
Employee Ownership Trust (EOT) Tax Exemption
The budget proposes a tax exemption on up to $10 million in capital gains for individuals selling their businesses to an EOT if certain criteria are met:
-
Sale of shares must be from a non-professional corporation.
-
The seller, or their spouse or common-law partner, must have been actively involved in the business for at least two years prior to the sale.
-
The business shares must have been solely owned by the seller or a related person or partnership for two years before the sale, and mainly used in active business.
-
At least 90% of the EOT’s beneficiaries must be Canadian residents after the sale.
-
If multiple sellers are involved, they must jointly decide how to divide the $10 million exemption
-
If the EOT doesn’t maintain its status or if the business assets used in active business drop below 50% at any point within 36 months after the sale, the tax exemption may be revoked.
-
For Alternative Minimum Tax purposes, the exempted gains will face a 30% inclusion rate.
-
The normal reassessment period for the exemption is extended by three years.
-
The measure now also covers the sale of shares to a worker cooperative corporation.
This exemption is valid for sales occurring from January 1, 2024, to December 31, 2026.
Home Buyers Plan (HBP)
The budget proposes enhancements to the HBP for 2024 and beyond, effective for withdrawals after April 16, 2024. These include:
-
Raising the RRSP withdrawal limit from $35,000 to $60,000 to support first-time homebuyers and purchases for those with disabilities.
-
Extending the grace period before repayment starts from two to five years for withdrawals made between January 1, 2022, and December 31, 2025, deferring the start of the repayment period and thereby providing new homeowners additional time before they need to commence repayments
Interest Deductions and Purpose-Built Rental Housing
The budget proposes a selective exemption from the Excessive Interest and Financing Expenses Limitation (EIFEL) rules for certain interest and financing expenses related to arm’s length financing. This exemption is for the construction or purchase of eligible purpose-built rental housing in Canada and applies to expenses incurred before January 1, 2036. To qualify, the housing must be a residential complex with either at least four private apartment units, each with its own kitchen, bathroom, and living areas, or 10 private rooms or suites. Additionally, at least 90% of the units must be designated for long-term rental. This exemption will be effective for tax years starting on or after October 1, 2023, in line with the broader EIFEL regulations.
Accelerated Capital Cost Allowance (CCA) – Purpose built rental housing
The budget introduces an accelerated CCA of 10% for new rental projects that start construction between April 16, 2024, and December 31, 2030, and are completed by December 31, 2035. This accelerated depreciation applies to projects that convert commercial properties into residential complexes or expand existing residential buildings that meet specific criteria under the EIFEL rules. However, it does not cover renovations to existing residential complexes.
Additionally, these investments will benefit from the Accelerated Investment Incentive, which allows for immediate depreciation deductions for properties put into use before 2028. Starting in 2028, the regular depreciation rules, including the half-year rule, will apply.
Accelerated Capital Cost Allowance (CCA)- Productivity-enhancing assets
The budget introduces immediate expensing for newly acquired properties that become operational between April 16, 2024, and December 31, 2026. This applies to specific categories such as:
-
Class 44- Patents and rights to patented information
-
Class 46- Data network infrastructure and related software
-
Class 50- General electronic data-processing equipment and software
Properties that are put into use between 2027 and 2028 will continue to benefit from the Accelerated Investment Incentive.
To qualify for this accelerated depreciation, the property must not have been previously owned by the taxpayer or someone closely connected to them, and it must not have been received as part of a tax-deferred deal. Also, if a tax year is shorter, the depreciation will be adjusted accordingly and will not carry over to the next year.
Canada Carbon Rebate for Small Businesses
The budget introduces a Canada Carbon Rebate for small businesses, offering a new refundable tax credit automatically. To be eligible, a Canadian-controlled private corporation must:
-
File a tax return for its 2023 tax year by July 15, 2024, for the fuel charge years from 2019-20 to 2023-24. For subsequent fuel charge years, it must file a tax return for the tax year that ends within that fuel charge year.
-
Employ 499 or fewer people across Canada during the year that corresponds with the fuel charge year.
The amount of the tax credit for each eligible business will depend on:
-
The province where the company had employees during the fuel charge year.
-
The number of employees in that province multiplied by a rate set by the Minister of Finance for that year.
-
The CRA will automatically calculate and issue the tax credit to qualifying businesses.
We can help!
Wondering how this year’s budget will impact your finances or your business? We can help – give us a call today!








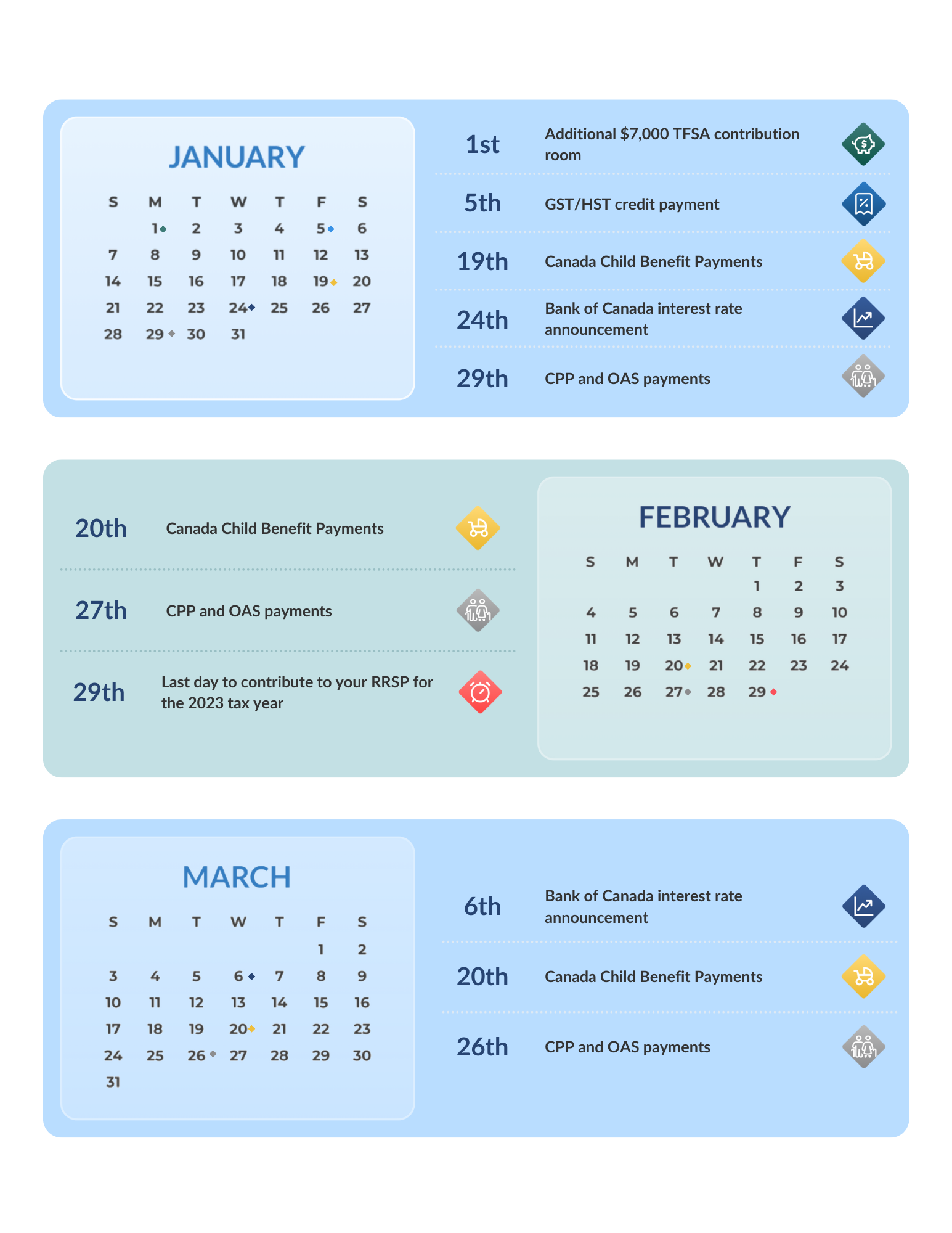
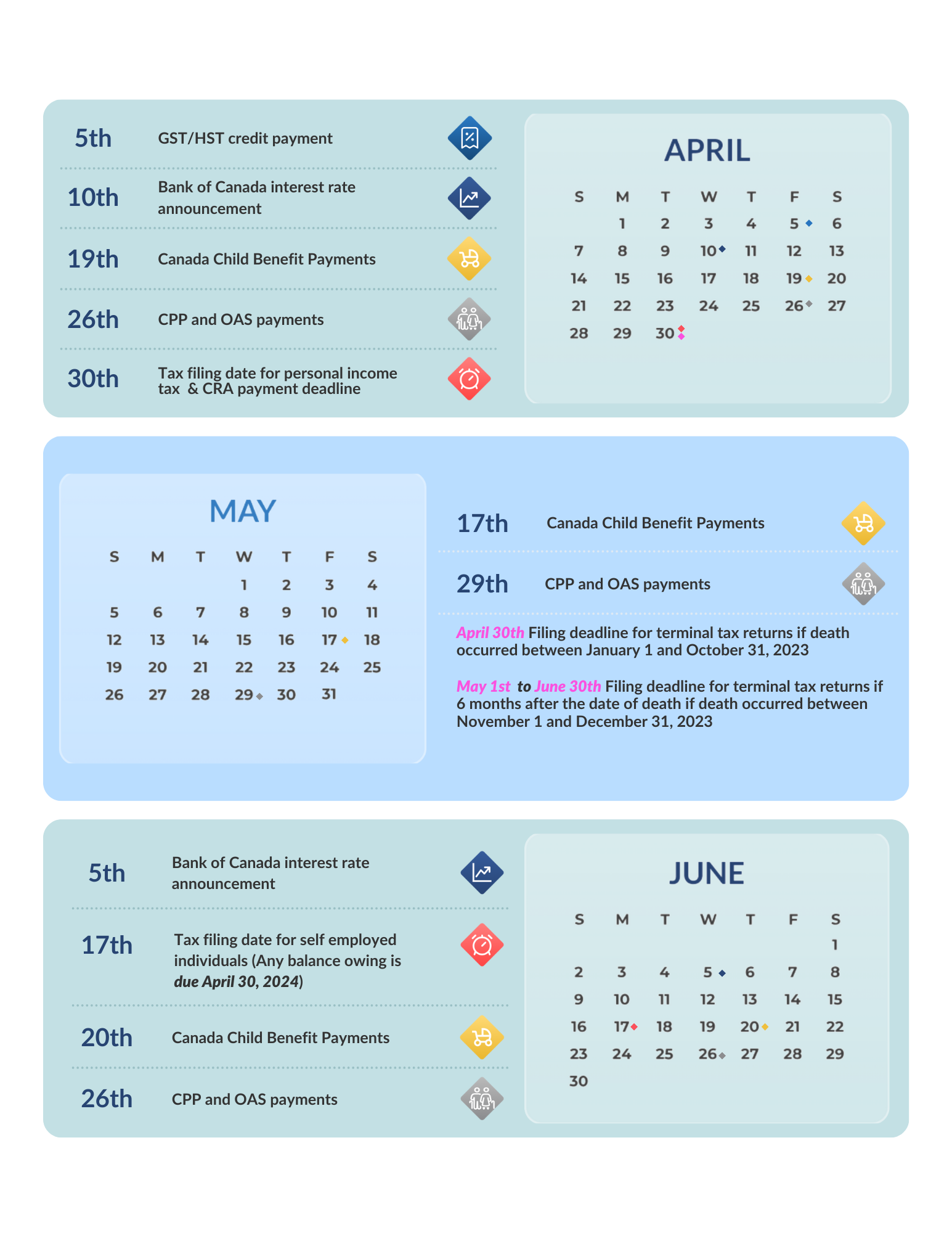




%20in%20Canada.jpg)



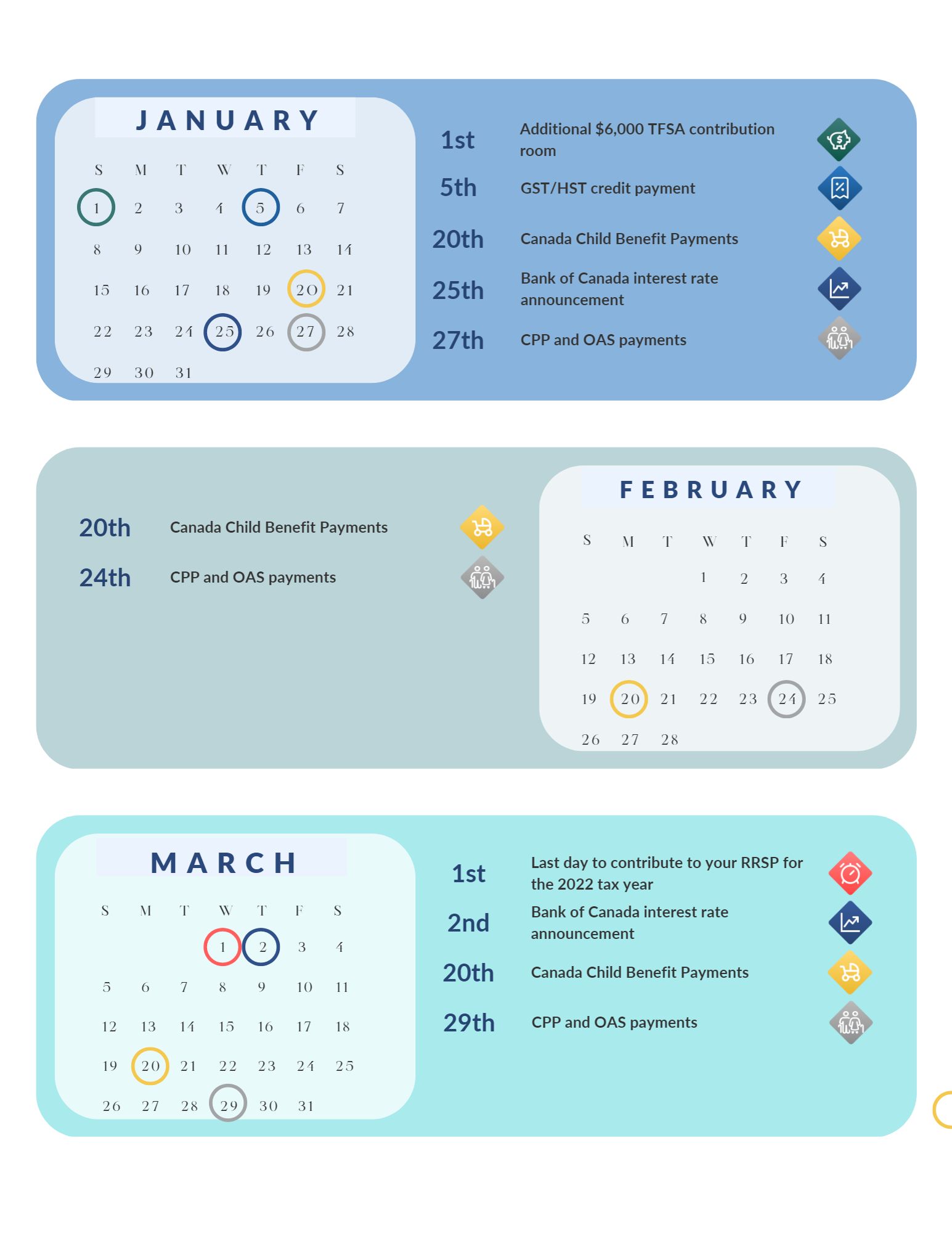
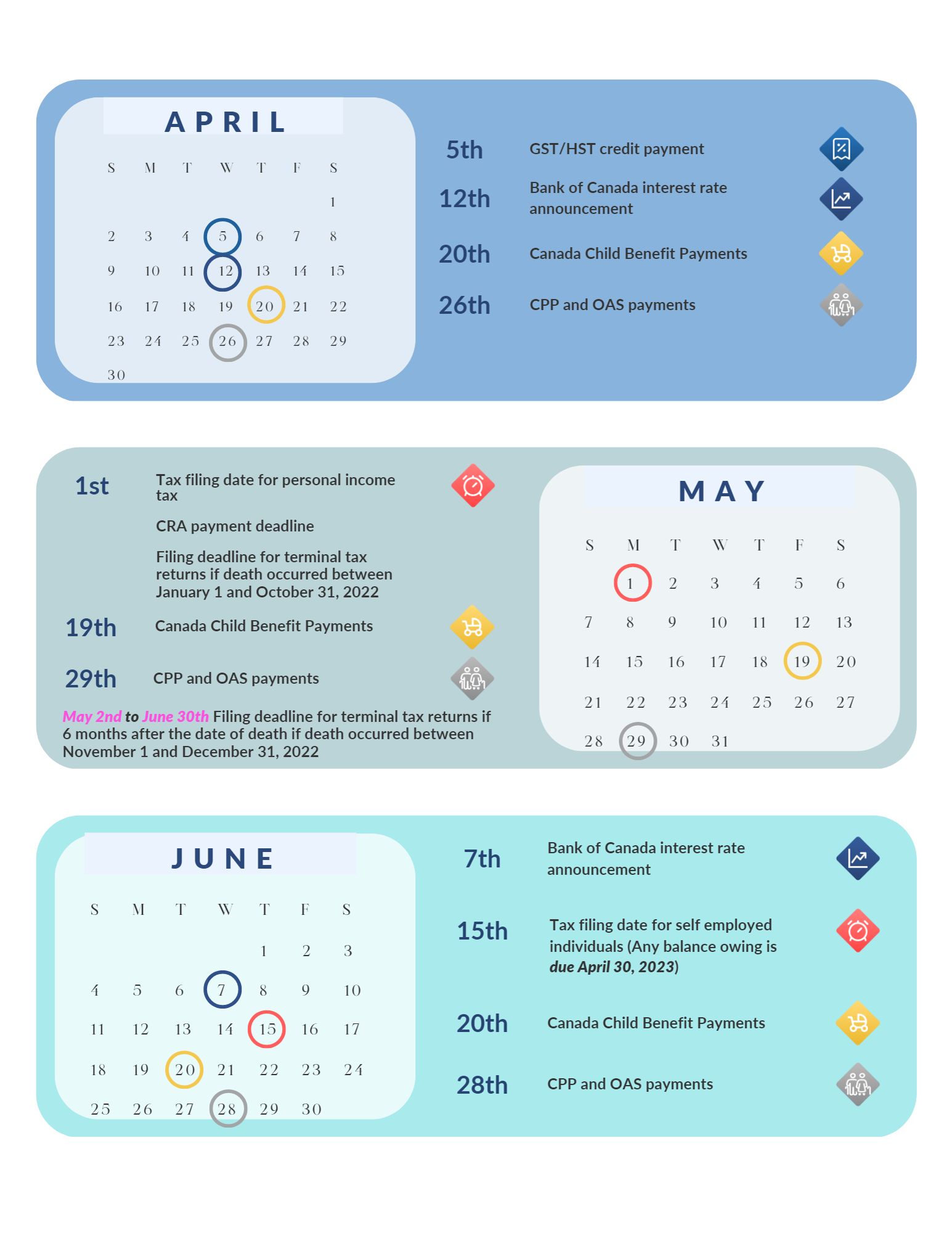





-Tracy%20-Duff-JoSXuxaB9D3svbujB.png)